After a series of meetings on VHF subjects in our HF5L club, we started to prepare for work through amateur satellites.
March 8, 2019 Piotr SQ5JUP made the first contact from home QTH via FOX-1D satellite (AO-92) on FM using the X300 antenna + duplexer MX-72A + IC-9100. As you can see, you can do without a directional antenna!
Mirek SP5GNI prepares and tests hardware and software at home. As of March 12:
– own construction controller for the azimuth/elevation RAS rotor (based on the new GNI-r5 controller). The controller uses the AlfaSpid protocol and is compatible with satellite tracking programs, such as Orbitron or SatPC32
– launching the rotor/controller/Orbitron set “on the table”
– installation of the SatPC32 program; it is much newer and better than Orbitron, it allows automatic compensation of the Doppler effect
– assembly of rotor and two-band 16 el. antenna in the garden
– launching the set antena/rotor/controller/ T-991/SatPC32
– listening stations working via satellites (SSB, CW, FM)
– March 13 at 11:03 local time – Mirek makes first FM contacts via FOX-1D (AO-92) with PD4HDB and SQ2XE (big emotions, as always when the first time)
– March 17, 2019 – making of a 75-ohm cable with symmetrators and a line fitting two Yagis for 70 cm band
 – assembling 2 antennas (made by SP5CIB) on the boom. Antennas are offset by 1/4 lambda from each other. This gives circular polarity. Such configuration results in a loss of 3 dB in relation to a single antenna, but thanks to this, polarization fades that can reach in theory up to 20 dB are eliminated
– assembling 2 antennas (made by SP5CIB) on the boom. Antennas are offset by 1/4 lambda from each other. This gives circular polarity. Such configuration results in a loss of 3 dB in relation to a single antenna, but thanks to this, polarization fades that can reach in theory up to 20 dB are eliminated
– March 18 – test QSOs in a configuration with two FT991 radios. The SatPC32 program deals with rotor control and Doppler correction for both transceivers. The biggest achievement is 4 stations on FM with one SO-50 pass. It is one of the few satellites which has a downlink of 70 cm. Antennas have worked, but I thought that it would be better to hear. However, the preamplifier would not hurt. Definitely no quality for the 2 m band, 6 vertical elements are not enough – crossed yagi is a must!
– March 27 – receiving and the first successful decoding of frames from the PW-Sat2 satellite. This satellite is temporarily in low activity, charging the batteries. It sends a package somewhere like every minute
– March 28 – after mounting the antennas on the metal boom, the DBA270 preamplifier and the MX72N duplexer were installed on the mast. Thanks to this, it is possible to work on one FT991 in split on two bands with one coaxial cable. It works! We ordered a crossed yagi antenna for 2m.
– using our antenna system and FUNCube Pro + every now and then I can easily pick up, record and upload the received packets from PW-Sat2. I got QSL from the PW-Sat team!
– April 5 – receiving RTTY signals (70 cm) and SSTV (2 m) from a balloon released by the SP3KEH team in Poznań
– April 9 – installation and wiring of the Crossed Yagi 2×7 el (WiMo) antenna. The first tests were excellent, SWR = 1.0, the satellites are really heard good
– April 13 – work without the DBA270 preamplifier (broken down). From April 11, ISS broadcasts SSTV images ( https://issfanclub.eu/2019/04/07/ariss-sstv-event-planned-with-special-award/ ). It is not easy to stick in time with the right trajectory and solve technical problems during a 10-minute flight. In addition, there were problems on the transmitting side – audio modulation very quiet. No luck to pick up any image in its entirety, the best three are shown below.
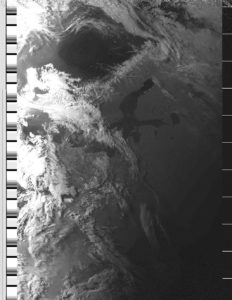
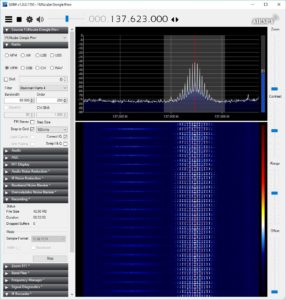
– April 24 – apart from amateur satellites, a lot of other scrap metal is flying over us, including meteorological satellites. NOAA satellites take photos continuously and it is relatively easy to receive from them. Using our antennas for tracking and FUNCube Pro + for reception, I recorded the signals broadcast by NOAA-15 on channel 137,620 MHz, when it flew over Poland today at 18:30. Kuba (my son) decoded the signals and generated photos using the article HERE (from chapter 5go). Here are the effects (left photo in visible light, on the right in infrared), and the SDRSharp window:
– May 1 – we celebrated the labor day with a set of satellite antennas and a rotor installed on the lawn near the HF5L club. The participants were: Wojtek SP5DPD, Mirek SP5GNI, Sławek SP5ICS, Marek SP5ISZ, Marek SP5IXS and Grzegorz SP5MI. Although only 7 QSOs could be made via satellites, the system tests should be considered successful. The next step is the final installation of the antenna system on the roof.
– June 13 2019 – it’s time for Oscar 100! See the new thread HERE.
– January 30/31 2020 – ISS again transmits SSTV pictures. The signal was strong, you could try on any antenna (145.800 MHz, FM, set Auto in the MMSSTV RX application – it switched itself to PD120). Here’s what I received on the not-movable vertical 4 elements Yagi antenna:
The coronavirus outbreak has frozen club activities, including the installation of antennas for low-orbitting satellites. The ISS is still transmitting, there are as many as 4 hams on the current shift. On December 2, 2020, they were transmitting SSTV images again – here’s what we managed to catch up:
Until the possibility of installing a rotor antenna set at the HF5L club, it was installed in the home QRA SP5GNI in May 2021.
The mast was attached to the chimney on the roof. A RAS azimuth/elevation rotor was mounted on it. The 2m antenna was Crossed Yagi 2×7 elements, the 70cm band uses 2 antennas 13-elements yagis. Antennas through the MX72N duplexer are connected to DBA270 RX LN preamplifier. This allowed the use of a relatively high-loss H155 coaxial cable, which in turn has the advantage of small diameter and ease of installation.
The new UHF/VHF shack consists of FT991, GNI-r9 rotor controller (SP5GNI design) and a laptop with SatPC32 software installed. The first attempts were successful – in one pass of the RS-44 satellite 8 QSOs was done – from EA to UA0.
On 5-9 August 2021, the HF5L club worked via the QO-100 satellite from Ciechanowiec KO12fq under the sign of HF5L/p. Equipment: FT991, DX-Patrol up-converter, PA 4W, POTY antenna, 80 cm platter, RTL-SDR dongle + SDR Console software (140 QSO, including PY, VU, ST, A71, V51)..
The HO-113 CAMSAT XW-3 (CAS-9) satellite carrying a 145/435 linear transponder was launched on December 26, 2021. The functions of XW-3 (CAS-9) satellite include UHF CW telemetry beacon, GMSK telemetry data transmission, V/U mode linear transponder, a visible light band space camera and an experimental thermoelectric generator for high school students.
For proper SatPC32 operation you need to add the line in Doppler.SQF file:
HO-113,435180,145870,USB,LSB,REV,0,0
and the line in AmsatNames.txt file:
50466 21131B HO-113
Both files could be found in menu: ? – Auxiliary Files
20 February 2022 between 05:12 UTC and 11:51 ARISS Europe and ARISS USA teams performed special SSTV Experiment using a new SSTV digital coding scheme. The first experiment in the series utilized ARISS approved ground stations in Europe that transmited these digital SSTV signals. The used modulation was 4L-FSK. For the decoding of the 320 x 240 px images, the software KG-STV was required – see for example here:
http://www.g0hwc.com/kg-stv-english.html .
Using the above-described shack designed to work with low-orbital satellites (FT991, GNI-r9 controller and a laptop with SatPC32 and KG-STV software), I decided to take part in this experiment. Below are 3 pictures taken during one of the flights:
Unfortunately, none of the received images is complete. This was due to interruptions in transmission and disruptions in reception. Despite an appeal to the amateur radio community to refrain from using an ISS voice repeater during the experiment, some colleagues did not comply.
On June 8, 2022 I was able to make a QSO with VE1CWJ (Canada, 5865 km), and on July 5, 2022 with ST2NH (Sudan, 4206 km) – both via RS-44.
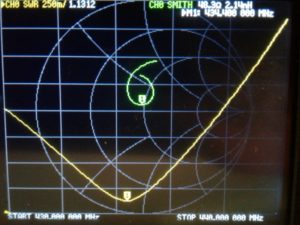
In September 2022, I decided to check the behavior of the system with a different 70 cm antenna. I was not satisfied with the operation of 2 Yagi antennas, 13 elements each configured to work with circular polarization. I installed a horizontally antenna borrowed from the SQ5JUP and found the system to perform better. I decided to convert the antenna system into 2 Yagi antennas, 13 elements each (by SP5CIB) mounted one above the other. I checked the antennas on 70 cm with NanoVNA. I noticed a very large influence of the distance between the antennas on the SWR. After moving to the maximum possible distance for mechanical reasons, I got quite a decent result: SWR = 1.13 for f = 434,400 MHz.
To attach 2 antennas to the boom, I used typical metal elements from a DIY store.
In October 2022, Adam SP5UFK decided to try his hand at satellite communications. After all, you can try QSO via low-orbital satellites without even having a complex system with azimuth and elevation rotation. Some satellites, such as RS-44, SO-50, ISS, are so “strong” that you can work with an ordinary yagi antenna or even with a vertical antenna. Adam installed a dual band antenna 3el. + 5el for communication via satellites to support the X300 vertical antenna, which could not cope with longer distances.
In one day he managed to do QSOs with the following countries:
ISS: PD5 (FM) , SP2 (FM), EA1 (FM)
RS-44: EA1 (SSB), IK2 (SSB), DC1 (SSB)
AO-91: SP2 (FM)
FO-29: EA1 (CW)
On October 25, 2022 via RS-44 I managed to make a QSO with BG0CAB (China, 4855 km), which was confirmed by a beautiful digital QSL card.
On December 1, 2022, I started my adventure with the new GreenCube satellite and a new mode of operation. The spacecraft has been launched on 13 July 2022 and it has been deployed in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) at approximately 6000 km of altitude. GreenCube telecommunication subsystem has a digipeater functionality available to the radioamateur community. The GreenCube satellite is also named IO-117.
Getting my system up and running with the FT991 was not difficult. Details can be found:. https://hf5l.pl/satelita-grencube/
The first contact was made with ST2NH (thank you, Nader for another satellite!). Below are screenshots from the GUI window. My QSO in bold:
[02/12 20:18:01.037] Received: EA3EA>SM0TGU, GreenCube, STORE=0 UR 599 JN01um QSL? [02/12 20:18:06.832] Received: S57NML>OK2UZL, GreenCube, STORE=0 JN76OD [02/12 20:18:11.528] Received: OK2UZL>ES4RM, GreenCube, STORE=5 599 JN79sa op.Ludek [02/12 20:18:12.631] Received: Beacon 02/12 19:18:09.990 [02/12 20:18:20.532] Received: G0ABI>ALL, GreenCube, STORE=0 CQ IO80bu [02/12 20:18:28.944] Received: OK2UZL>S57NML, GreenCube, STORE=5 599 JN79sa op.Ludek [02/12 20:18:42.712] Transmitted: SP5GNI>ST2NH, GreenCube, STORE=0 UR599 KO02li [02/12 20:18:54.437] Received: IK7EOT>ES4RM, GreenCube, STORE=0 JN80PJ 599 QSL ? [02/12 20:18:58.136] Received: Alt. Beacon 02/12 19:18:55.384 [02/12 20:19:02.930] Received: IW7DOL>OK2UZL, GreenCube, STORE=0 599 JN90ci QSL? [02/12 20:19:11.635] Received: ST2NH>SP5GNI, GreenCube, STORE=0 RR 5NN TU [02/12 20:19:22.027] Received: DL5GAC>CQ, GreenCube, STORE=0 JN47UT [02/12 20:19:26.036] Received: IK7EOT>ES4RM, GreenCube, STORE=0 TNX QSO 73 TU [02/12 20:19:27.127] Received: EA3EA>EA3BT, GreenCube, STORE=0 UR 599 JN01um QSL? [02/12 20:19:42.631] Received: Beacon 02/12 19:19:40.012 [02/12 20:19:45.037] Received: OK2UZL>IW7DOL, GreenCube, STORE=5 599 JN79sa op.Ludek [02/12 20:19:46.136] Received: EA3EA>SM0TGU, GreenCube, STORE=0 UR 599 JN01um QSL? [02/12 20:19:55.637] Received: OK2UZL>IW7DOL, GreenCube, STORE=5 599 JN79sa op.Ludek [02/12 20:20:07.532] Transmitted: SP5GNI>ST2NH, GreenCube, STORE=0 TNX first QSO! [02/12 20:20:17.033] Received: EA7KI>ALL, GreenCube, STORE=1 CQ CQ EA7KI IM76RR [02/12 20:20:20.925] Received: EA3EA>ES4RM, GreenCube, STORE=0 UR 599 JN01um QSL? [02/12 20:20:48.028] Received: IK7EOT>EA7KI, GreenCube, STORE=0 JN80PJ 599 QSL ?
In July 2023, Adrian SQ5Z took up satellite communications, mainly via APRS, because he could not break through with his 5W on the phone. As for APRS, the matter is relatively simple. When the ISS is about 25 degrees above the horizon, frames start flying. You can pick up a few to a dozen of them during the flight. Some characters are almost constant, i.e. frames appear during almost every flight.
The entrance to the ISS is worse, although not as much as in the case of phone. Adrian succeeded on the third time, and then he entered almost always (i.e. he got his own frame from the ISS).
Contact with the ISS can be found on the following websites:
http://www.ariss.net/index.cgi
http://www.findu.com/
Two-way QSOs are unlikely, because it is difficult to answer via the ISS after receiving a frame from the ISS – too little time. Sometimes the parties confirm receipt of frames via arris.net, qrz.com .
Sample exchange of confirmations (http://www.findu.com/):
| SQ5Z | ON7BRT | 07/28 20:16:08z | Send another | All the best wishes to you! 73! Of course QSL (via bureau). |
| ON7BRT | SQ5Z | 07/27 16:43:22z | Reply | Heard via ISS 16.29 UTC, 73! QSL VIA BUREAU |
It follows that ON7BRT got a frame from Adrian via the ISS. Adrian didn’t get a frame from him.
Adrian did not use a computer, although that would greatly increase the possibilities (e.g. during the flight there is no chance to edit text on a handheld radio – it’s not a problem on a computer). Only used FT5D with handheld directional antenna.
To play with the ISS, you can use the UISS program (https://www.qsl.net/on6mu/uiss.htm). This is a great, free program designed to communicate with UI packages over the ISS, and for a small donation you can run interesting extensions.
more tbd.
Miro SP5GNI































Leave a Comment